

어릴 때 물속에 이게 많아서 자주 보기도 했고, 뜯어서 뿌리를 먹기도하고 살았다.
잘피라고 하는구나..
고향(경남 남해)에선 '진지' 라고 불렀는데 표준어로 뭐라고 하는지 몰라서 못찾았는데,
우연히 다큐에서 보고 이름을 알게 돼서 또 까먹을까봐 올려놓기..
이미지 얻어온 곳에 보니 고향에서만 먹고 산게 아니구나 싶다..



int to C-style (NULL-terminated char[]) string
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8: 9: 10: 11: 12: 13: |
int n=1234567890; |
int to ATL/MFC CString
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: |
#include <cstringt.h> |
int to STL std::string
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8: 9: |
#include <iostream> |
C-style (NULL-terminated char[]) string to int
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: |
#include <stdlib.h> |
ATL/MFC CString to int
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: |
#include <cstringt.h> |
STL std::string to int
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: |
#include <string> |
1: 2: |
0 to 4,294,967,295 (unsigned) |
1: 2: |
0 to 18,446,744,073,709,551,615 (unsigned) |
| 64비트 정수 __int64 사용법: 변수 선언, printf()로 출력 (0) | 2012.01.12 |
|---|---|
| int to long long type casting (0) | 2012.01.09 |
| 정수 실수 종류(자료형;데이터형), 최소값 최대값; char int float, Data Type Ranges (0) | 2011.11.25 |
| [Link Error] LIBC.lib 등의 정확한 사용 (0) | 2011.09.17 |
| [Link Error] LIBCMT.lib(invarg.obj) (0) | 2011.09.17 |
public void EnumInstanceFromString() { // The .NET Framework contains an Enum called DayOfWeek. // Let's generate some Enum instances from strings. DayOfWeek wednesday = (DayOfWeek)Enum.Parse(typeof(DayOfWeek), "Wednesday"); DayOfWeek sunday = (DayOfWeek)Enum.Parse(typeof(DayOfWeek), "sunday", true); DayOfWeek tgif = (DayOfWeek)Enum.Parse(typeof(DayOfWeek), "FRIDAY", true); lblOutput.Text = wednesday.ToString() + ". Int value = " + ((int)wednesday).ToString() + "<br>"; lblOutput.Text += sunday.ToString() + ". Int value = " + ((int)sunday).ToString() + "<br>"; lblOutput.Text += tgif.ToString() + ". Int value = " + ((int)tgif).ToString() + "<br>"; }
Wednesday. Int value = 3 Sunday. Int value = 0 Friday. Int value = 5
| Nullable 형식 사용 (0) | 2012.01.19 |
|---|---|
| MeasureString(문자열 길이 체크) (0) | 2012.01.17 |
| 문자열이 숫자 값을 나타내는지 확인 (0) | 2011.12.16 |
| Operator Overloading in C# (2) | 2011.12.05 |
| Force property update in propertygrid (0) | 2011.11.29 |
문자열이 지정한 숫자 형식의 유효한 표현인지 확인하려면 모든 기본 숫자 형식에서 구현되며 DateTime 및 IPAddress 같은 형식에서도 구현되는 정적 TryParse 메서드를 사용합니다. 다음 예제에서는 "108"이 유효한 int인지 확인하는 방법을 보여 줍니다.
int i = 0; string s = "108"; bool result = int.TryParse(s, out i); //i now = 108
문자열에 비숫자 문자가 포함되어 있는 경우 또는 숫자 값이 지정한 특정 형식에 비해 너무 크거나 너무 작은 경우 TryParse는 false를 반환하고 out 매개 변수를 0으로 설정합니다. 그렇지 않으면 true를 반환하고 out 매개 변수를 문자열의 숫자 값으로 설정합니다.
문자열은 숫자만 포함할 수 있으며 사용할 TryParse 메서드 형식에 아직 유효하지 않을 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 "256"은 byte에 대해서는 유효한 값이 아니지만int에 대해서는 유효한 값입니다. 이때 98.6"은 int에 대해 유효한 값이 아니지만 decimal에 대해서는 유효한 값입니다. |
다음 예제에서는 long, byte 및 decimal 값의 문자열 표현을 사용하여 TryParse를 사용하는 방법을 보여 줍니다.
string numString = "1287543"; //"1287543.0" will return false for a long long number1 = 0; bool canConvert = long.TryParse(numString, out number1); if (canConvert == true) Console.WriteLine("number1 now = {0}", number1); else Console.WriteLine("numString is not a valid long"); byte number2 = 0; numString = "255"; // A value of 256 will return false canConvert = byte.TryParse(numString, out number2); if (canConvert == true) Console.WriteLine("number2 now = {0}", number2); else Console.WriteLine("numString is not a valid byte"); decimal number3 = 0; numString = "27.3"; //"27" is also a valid decimal canConvert = decimal.TryParse(numString, out number3); if (canConvert == true) Console.WriteLine("number3 now = {0}", number3); else Console.WriteLine("number3 is not a valid decimal");
| MeasureString(문자열 길이 체크) (0) | 2012.01.17 |
|---|---|
| Convert String To Enum Instance (0) | 2011.12.16 |
| Operator Overloading in C# (2) | 2011.12.05 |
| Force property update in propertygrid (0) | 2011.11.29 |
| is 비교 연산자, as 연산자 (0) | 2011.11.29 |
흠.. 완충과 완방은 한달에 한번만.. 이건 아닌데요..
요즘엔 밧데리가 마니 좋아졌죠 그래서 완충은 상관없는데 완방은... 리튬 밧데리에 사용기간을 단축 시킨다고 알고 있습니다. 그렇기때문에 충전을 할수 있으면 계속 하는게 밧데리 수명에 도움이 됩니다.
그러니깐 왠만하면 생각 날때마다 충전하세요 핸드폰도 마찬가지입니다. 다쓸때까지 기다리는거 보다는
충전 할수 있을때 계속 충전해주세요 그게 밧데리 기간을 늘려주는 방법입니다.
- 이정도만 지켜도 오래쓸꺼에요-
1. 완전 방전 금지
2. 충전 가능한 곳에서는 충전기에 연결해둔 상태로 외부전원으로 사용.
| Anti 'Shut Down' (1) | 2012.02.08 |
|---|---|
| [링크] 우리나라 IT 업체가 소프트웨어 설계를 하면 안 되는 이유(?) (0) | 2012.02.08 |
| [펌] 자랑스러운, 위대한 대한민국 史 (0) | 2011.11.16 |
| [펌] 파랑새 신드롬 (0) | 2011.11.16 |
| 눈에 좋은 색 (1) | 2011.10.19 |
Description
The Source code below shows how to use OperatorOverloading in C#. Operator Overloading is pretty useful concept derived from C++ by C#.For eg.
We can have class Matrix which hold 2D array of elements.C# add doest not Allows us to do Addition, Subtraction of matrices using the +,- operator rather We use to write Methods AddMatrix(),SubMatrix() with the use of Operator.
Overloading we make the user to code it:
M3=M1+M2 where M1 and M2 are matrix objects.
Some Tips while using Operator overloading:
Source Code:
// Source Code starts
using System;
class Square
{
private double Side;
//public Constructor if int is passed convert to double and assign to Side
public Square(int s)
{
Console.WriteLine(".ctor with int argument");
Side=(double)s;
}
//OverLoaded constructor with double argument
public Square(double s)
{
Console.WriteLine(".ctor with double argument");
Side=s;
}
//override ToString() method of object class.
public override string ToString()
{
Console.WriteLine("Override object class's string");
return this.Side.ToString();
}
//Overloading + operator to add 2 square objects and return new square object
public static Square operator + (Square x,Square y)
{
Console.WriteLine("Overloading + with Square,Square");
return new Square(x.Side+y.Side);
}
//Overloading + operator to add square objects with double side and return new square object
public static Square operator + (Square x,double y)
{
Console.WriteLine("Overloading + with Square,double");
return new Square(x.Side+y);
}
//Overloading + operator to add square objects with int side and return new square object
//This is not necessary since C# automatically calls +(Square,double)
public static Square operator + (Square x,int y)
{
Console.WriteLine("Overloading + with Square,int");
return x +(double)y;
}
public static implicit operator Square(double s)
{
Console.WriteLine("Overloading = for Square s5=1.5 assignment");
return new Square(s);
}
public static implicit operator Square(int s)
{
Console.WriteLine("Overloading = for Square s5=10 assignment");
return new Square((double)s);
}
//OverLoading == operator
public static bool operator ==(Square x,Square y)
{
Console.WriteLine("Overloading == with Square,Square");
return x.Side==y.Side;
}
//OverLoading != operator
public static bool operator !=(Square x,Square y)
{
Console.WriteLine("Overloading != with Square,Square");
return !(x==y); //This will call to operator == simple way to implement !=
}
//Always override GetHashCode(),Equals when overloading ==
public override bool Equals(object o)
{
return this==(Square)o;
}
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return (int)Side;
}
//OverLoading > operator
public static bool operator >(Square x,Square y)
{
Console.WriteLine("Overloading > with Square,Square");
return x.Side>y.Side;
}
//OverLoading < operator
public static bool operator <(Square x,Square y)
{
Console.WriteLine("Overloading < with Square,Square");
return x.Side<y.Side;
}
//OverLoading <= operator
public static bool operator <=(Square x,Square y)
{
Console.WriteLine("Overloading <= with Square,Square");
return (x<y) || (x==y); //Calls to operator == and <
}
//OverLoading >= operator
public static bool operator >=(Square x,Square y)
{
Console.WriteLine("Overloading >= with Square,Square");
return (x>y) || (x==y); //Calls to operator == and >
}
//Readonly Property
public double Area
{
get
{
return 2*Side;
}
}
public static void Main()
{
Square s1=new Square(10);
Square s2=new Square(20);
Square s3=s1+s2; // This will call operator + (Square,Square)
Console.WriteLine(s3);
Console.WriteLine(s3+15); // This will call operator + (Square,int) and then ToString()
Console.WriteLine(s3+1.5);// This will call operator + (Square,double) and then ToString()
s3=10; // This will call operator Square(int)
Console.WriteLine(s3);
Square s4=10;
Console.WriteLine(s1==s4); //Calls == operator
Console.WriteLine(s1!=s4); //Calls != operator
Console.WriteLine(s1>s2); //Calls > operator
Console.WriteLine(s1<=s4); //Calls <= operator
}
}
// Source Code End
| Convert String To Enum Instance (0) | 2011.12.16 |
|---|---|
| 문자열이 숫자 값을 나타내는지 확인 (0) | 2011.12.16 |
| Force property update in propertygrid (0) | 2011.11.29 |
| is 비교 연산자, as 연산자 (0) | 2011.11.29 |
| effective c# - 1 (0) | 2011.11.29 |
마인드맵 선택 기준
① 무료여야 한다.
② 한글판이어야 한다.
③ 인지도가 높은 제품이여야 한다.
* 이 세가지를 모두 충족하는 제품은 2가지임.
Freemind , 알마인드
1. Freemind 한글판/ 한글 설정 방법
무료 마인드맵,Freemind ,왜 마인드 맵이 필요할까?
국내용 버젼도 있고 웹용 무료 마인드 맵 버젼도 다양하게 있는데
아래 소개하는 버젼은 완전무료 버젼으로 소스 공개되어 제공되어 한글화가 된 무료 마인드맵으로
사용하기 쉽고 잘 구성되어진 무료 마인드맵 유틸이다
얼핏보면 영문버젼 같은데 한글이 지원되는 다국어 버젼용 무료 freemind 맵이다
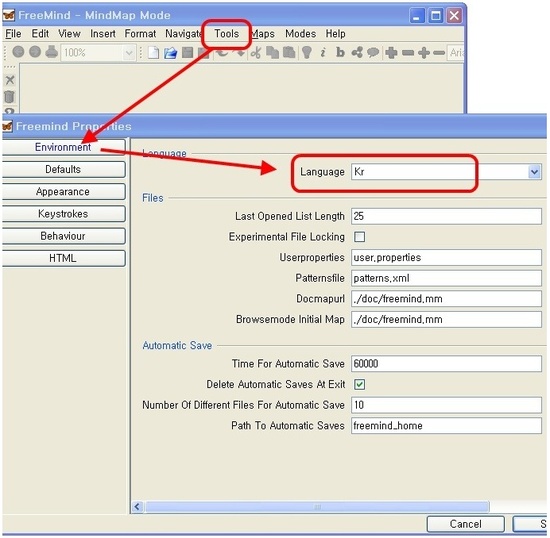
한글로 메뉴를 변경하려면 아래 처럼 Tools -Preference-Environment-language 에서
KR로 변경해 주고 Freemind를 재시작 해 주면 한글이 반영된다
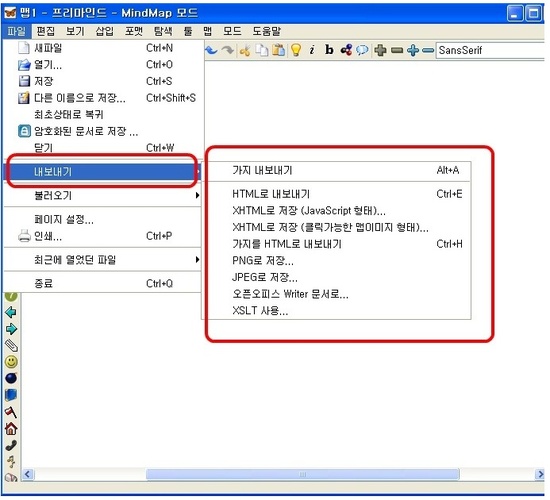
ㅇ내보내기를 하면
html,xhtml과 PNG 저장 , JPEG 그림형태로 저장이 가능하다
마인드 맵을 사용하기에도 편리하게 되어 있는데 메뉴얼을 확인하려면
영문버젼이 조금 아쉬운데 사용자 기반 중심으로 쉬운 인터페이스이고 무료버젼이라고 하여도
상당히 잘 만들어젼 프로그램이다 소스도 약 3M 정도이고
http://freemind.sourceforge.net에서 다운로드 하여 사용할 수 있다
마인드 맵은 왜 필요할까? 마인드맵의 필요성
1.창의성이 필요로 한 일을 시작 할 때 자료를 효과적으로 정리하고
체계화시켜 정리할 수 있다
2.아이디어가 생각이 나지 않거나 마구잡이로 나열된 자료를 효과적으로 정리할 수 있다
또한 브레인스토밍 되어진 자료들을 체계화 요약이 가능하다
3. 업무의 프리젠테이션 미팅 할 때, 마인드맵으로 설명을 하게 되면 쉽게 명확한 의사전달이 가능하고
마케팅 할 때 개선해야 할 문제점도 짚어 낼 수도 있고 회사의 업무 활용에 아주 중요한 도구가 될수 있다
2. 알마인드
http://www.altools.co.kr/Product/ALMind_Intro.aspx
알툴바, 알집, 알약을 만드는 이스트소프트 에서 만들었습니다.
2011.10월에 배타버전을 출시 했는데
무료임에도 내용이 상당히 충실하고 편리한 인터페이스를 갖었습니다.
상단 주소에서 다운 가능합니다.
알마인드는 직관적인 사용법으로 사용법이 쉽습니다.
[출처] Freemind 한글판/ 한글 설정 방법/알마인드/마인드맵추천|작성자 하박사
| HxD - Freeware Hex Editor and Disk Editor (0) | 2012.04.29 |
|---|---|
| FileTypesMan - File Types Manager for Windows (0) | 2012.04.18 |
| Sysinternals 툴 소개 (0) | 2011.10.26 |
| Reflector - 닷넷 사용하신다고요? 일단 리플렉터를 설치하세요. (0) | 2011.10.09 |
| DebugView for Windows - 이것없이 실행파일 디버깅을 하고 있다고요? 정말요? (0) | 2011.10.09 |
| 문자열이 숫자 값을 나타내는지 확인 (0) | 2011.12.16 |
|---|---|
| Operator Overloading in C# (2) | 2011.12.05 |
| is 비교 연산자, as 연산자 (0) | 2011.11.29 |
| effective c# - 1 (0) | 2011.11.29 |
| TreeNode Visual C# 도구 설명을 추가하는 방법 (0) | 2011.11.21 |
is 연산자 : 두 객체가 동일한지 비교하는데 사용, is 연산자는 해당 객체가 is 오른쪽 형식과 호환되는지 확인만 한다. 객체 형식을 변경할 수 는 없다.
as 연산자 : 객체가 호환되지 않으면 null 값을 할당, 호환되면 형식(casting)을 시켜준다. as 연산자는 강제 형변환과 비슷하며 변환시 예외가 발생하면 null을 채운다.
아래의 형태는 as 연산자가 하는 기능이다.
[표현식] is [데이터타입] ? (데이터타입)[표현식] : (데이터타입) null
| Operator Overloading in C# (2) | 2011.12.05 |
|---|---|
| Force property update in propertygrid (0) | 2011.11.29 |
| effective c# - 1 (0) | 2011.11.29 |
| TreeNode Visual C# 도구 설명을 추가하는 방법 (0) | 2011.11.21 |
| TreeView에서 Find 함수 사용 방법 (0) | 2011.11.20 |
String 비교는 불필요한 overhead를 포함하고 있다. 스트링이 비어 있는지를 체크하는 것이라면
Length properthy를 사용하도록 한다.
//NO
if ( str != "")//comparison of two strings {...}
//YES
if ( str.Length > 0) {...}C# string은 변경되지 않는다. string 값이 변경할 때, 아래와 같은 문제들이 야기된다.
//NO
String strConcat;
ArrayList arrayOfStrings = new ArrayList();
arrayOfStrings.Add("a");
arrayOfStrings.Add("b");
foreach (string s in stringContainer) {
strConcat += s;
}
//YES
StringBuilder sbConcat = new StringBuilder ();
foreach (string s in arrayOfStrings ) {
sbConcat.append(s);
}
BBoxing은 garbage-collected 힙 영역에 value types들을 저장하는데 이용된다.
value type이 box되면 새로운 ojbect가 메모리에 잡히고 생성되어야 한다.
즉, 아래의 두가지 작업이 일어난다.
- Object 인스턴스를 할당한다.
- 위 인스턴스에 value type 값을 복사해서 넣는다.
위의 이유로 되도록이면 Boxing을 피하는것이 좋다. ArrayList를 예로 들어보면 struct 키워드를
통해서 ArrayList의 값을 넣을 때 위와 같은 Boxing과 UnBoxing이 일어나게 된다.
//NO
struct st { public Int i; }
Arraylist arr = new ArrayList();
for (int i=0 ; i< count; i++) {
st s;
s.i = 4;
arr.item.add(st) ; //<- Boxing (Allocating an object instance
// + copying the value-type value into that instance)
}
st obj = (st ) arr[0]; //<- Unboxing (casting and copy)
//YES
//Decalre the data type as class.
Class st { public Int i; }== 보다 equal 함수를 사용하는것이 좀 더 빠르다.
string s1= "code";
string s2 = "code1";
//No:
if(s1 == s2){...}
//Yes:
if(s1.Equals(s2)){...}'foreach' 랑 'for' 키워드는 일부 비슷한 기능을 한다. - 블록 안에서 루프를 돌면서 기능을 수행
foreach와 for를 사용할때 가장 중요한 차이쯤은 루프문의 증가와 끝에 대해서 따로 작업이 필요 없다는것이다. 또한 foreach는 모든 collection을 사용할 수 있게 만들어졌다. foreach는for의 private한 case에 사용한다고 하기도 한다.
아래 코드를 통해서, 두 루프문이 동일한 결과를 낸다는것을 알 수 있다. 다만 foreach를 사용했을 경우퍼포먼스가 조금 떨어졌다. 좀더 무거운 변수와 큰 array를 사용하면 그 차이가 더 크게 날것이다.
foreach는 for에 비해서 좀더 사용하기 쉽지만 만약 큰 collection을 도는 경우는에는 'for' 를 사용하는것이 퍼포먼스에 좋을 것이다.
Code snippets:
//foreach
int[] arrayOfInts= new int[5];
int sum= 0;
foreach(int i arrayOfInts) {
sum+= i;
}
//for
int[] arrayOfInts= new int[1];
int sum= 0;
for(int i = 0; i < arrayOfInts.Length; i++) {
sum+= arrayOfInts[i];
}The 'as' operator does not throw an exception. In case of bad cast, the return value is null.
Code snippets:
//NO
object o = 1.3;
try
{
string str = (string)o;
}
catch(InvalidCastException ex){...}
//YES
string str = o as string;
if(null != str){...}Code snippets:
//NO
short shortNum;
int i = 32768;
shortNum = (short) i;
// problem after statment excution
// the shortNum variable has an uninitialized value,
//YES
try {
shortNum = checked((short)i); // solution
}
catch(OverflowException efx) {}Code snippets:
public class Preson{int nAge;}
//No:
static void main(object o){
try {
(Person)o.nAge = 45;
}
catch(InvalidCastException ex){...}
}
//Yes:
static void func(object o)
{
if ( true == (o is Person) )
{
(Person)o.nAge = 45;
}
}Implementing an interface explicitly 'hides' the interface methods. Visual Studio does not display the interface methods in the intellisense.
Code snippets:
//interface definition
Public interface IChild{
bool IsHuman();
void lie();
}
//class definition
Pubic Pinocchio: IChild {
IChild.IsHuman() //explicit interface implementation
{
}
public void Lie(); //regular interface implementation
}
//using the object
static void main()
{
// Visual studio will not display
// the isHuman mwthod in the intellisence.
Pinocchio o = new Pinocchio();
((IChild) o).IsHuman(); // using the IsHuman method explicitly.
o.Lie();
}Code snippets:
//Old way
String sFilePath = �c:\\a\\b\\c.txt�;
//The C# way
String sFilePath = @�c:\a\b\c.txt�;The CLS-Compliant attribute cause the compiler to check whether your public exposed types in the assembly are CLS-Compliant.
Prefer to define the attribute for the entire assembly, especially for API. The incentive to create a CLS compliant assembly is that any assembly written in one of the .NET aware languages can use your assembly more efficiently because there is no data types interoperability.
Code snippets:
using System;
[assembly:CLSCompliant(true)]You should define a destructor whenever you use native code in your assembly, i.e., use types that are not managed by the garbage collector. The compiler changes the destructor method to Finalize method (can be seen in the MSIL using the ILDasm.exe).
The Garbage collector marks a class with destructor as Finalized and calls the Finalize method while destructing the object. This behavior guarantees that your release of resources in the destructor will occur.
But, what if you want to release the resources immediately? For this purpose, you should implement the IDisposable interface and call theDispose method when you want to release the object.
Note 1: Do not use destructor if your class does not use native / unmanaged resources. If you do so, you create unnecessary work for the garbage collector.
Note 2: If you implement the IDisposable and a destructor, you should call the Dispose method from the destructor to force the object to release resources immediately.
Code snippets:
~my class {
if ( true == b) {
}
}
//The MSIL code:
protected override void Finalize() {
try {
if ( true == b) {
}
}finally { base.Finalize();}
}The GC.Collect method forces garbage collection of all generations.
The performance is hurt during the call to GC.Collect, the application execution is paused. Moreover, the method might cause the promotion of short lived objects to a higher generation, i.e., those object live longer than it should in the first place.
If you must use it in order to reclaim the maximum amount of available memory, use the method only on generation 0.
Code snippets:
//No:
GO.Collect();
//Yes:
GC.Collect(0);The attributes cause the compiler to pack the structure in sequential memory so that it can be sent to unmanaged code correctly (unmanaged code that expects a specific layout).
Code snippets:
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct st{
int i;
float f;
}What next?
The part II article, will deal with COM Interop in general, and events between managed and unmanaged code in particular.
출처 : http://www.cyworld.com/mengwi/7680825
| Force property update in propertygrid (0) | 2011.11.29 |
|---|---|
| is 비교 연산자, as 연산자 (0) | 2011.11.29 |
| TreeNode Visual C# 도구 설명을 추가하는 방법 (0) | 2011.11.21 |
| TreeView에서 Find 함수 사용 방법 (0) | 2011.11.20 |
| C# C++ COM Interop (0) | 2011.11.15 |