괴나리봇짐(개나리봇짐)
괴나리 봇짐의 어원은
괴나리 봇짐은 끈늘이 봇짐 즉 끈을 늘어뜨려 메는 보따리 짐이고 하여 끈늘이 봇짐이 끈느리봇짐 > 끠느리봇짐 > 긔느리봇짐 > 괴나리봇짐(개나리봇짐)으로 와전되어온 것이라고 합니다.
출처 : http://k.daum.net/qna/view.html?qid=0GEWc

괴나리 봇짐의 어원은
괴나리 봇짐은 끈늘이 봇짐 즉 끈을 늘어뜨려 메는 보따리 짐이고 하여 끈늘이 봇짐이 끈느리봇짐 > 끠느리봇짐 > 긔느리봇짐 > 괴나리봇짐(개나리봇짐)으로 와전되어온 것이라고 합니다.
출처 : http://k.daum.net/qna/view.html?qid=0GEWc
C#3.0이 등장 하면서 여러 가지 새로운 기능이 추가 되었습니다. 타입유추, 익명타입, 람다 표현식, 개체/컬렉션 초기화, Nullable 타입, 확장 메서드, 쿼리 키워드, 자동으로 구현된 속성(Automatic Property, 부분 매서드(partial method) 등등 상당히 많은 새로운 기능들이 추가 되었습니다. 이 기능 중 대부분의 기능은 LINQ의 기반이 되며 LINQ를 배우기 이전에 먼저 학습할 필요가 있습니다.
이번 강좌를 시작으로 앞에서 언급한 새로운 기능 중 LINQ의 기반이 되는 새로운 기능들에 대해 강좌를 연재 하려고 합니다. 언제 강좌가 마무리 될지 확실하지는 않지만 최대한 주기적으로 강좌를 연재하고 최대한 빠른 시간 안에 마무리 하도록 노력하겠습니다.
C# 3.0부터 지역 변수의 타입을 반드시 명시적으로 지정해줄 필요 없이 var키워드를 사용하여 컴파일러가 타입을 유추할 수 있도록 할 수 있습니다. 이는 뒤에서 배우게 될 명시적으로 타입을 지정하지 않는 익명 타입이나 가독성이 떨어지는 중첩된 제네릭(예: IEnumerable<IEnumerable<Product>>) 과 같이 특수한 경우에 var키워드를 사용하여 좀더 간단하게 타입을 표현할 수 있습니다.
다른 개발자가 코드를 보았을 때 이해 할 수 있는 수준으로 작성이 되면 var키워드를 통한 타입 유추는 좀더 간결한 코드를 만들어 낼 수 있는 훌륭한 기능이라 할 수 있겠습니다.
1. 타입유추는 어떻게 이루어 지는가?
var키워드는 변수를 선언하고 그 값을 할당하는 초기화 구문에서 '='을 기준으로 오른쪽 부분의 형태에 따라 컴파일러에게 타입유추를 지시 하게 됩니다.
위의 코드를 보면 5라는 값이 변수 i에 할당되므로 컴파일러는 5라는 값이 숫자 즉 int타입이라는 것을 미리 알고 있기 때문에 변수 i를 int타입으로 유추하게 되는 것 입니다.
C#의 기본 타입 뿐만 아니라 사용자 정의 타입(Class) 및 익명 타입(Anonymouse Type) 또한 유추 될 수 있습니다.
그럼 간단하게 사용자 정의 타입(Class)을 유추하는 코드를 살펴 보도록 하겠습니다.
Person이라는 새로운 Class를 만들고 개체를 생성한 후 var 키워드로 선언된 p라는 변수에 person개체를 할당하게 되면 컴파일러에 의해 변수 p는 Person타입으로 유추 됩니다.
익명 타입 또한 컴파일러에 의해 유추가 가능 합니다.
아래 코드를 보면 식의 오른쪽 부분이 익명 타입이고 그 타입을 변수 p가 받게 되면 컴파일러에 의해 변수 p는 익명 타입으로 유추가 됩니다.
위의 예제 코드에서는 익명타입의 형태만 알아 두고 자세한 내용은 다음 강좌에서 자세히 알아 보도록 하겠습니다.
다음은 쿼리표현식의 타입을 유추하는 코드 입니다.
위의 쿼리 표현식은 LINQ를 활용함에 있어서 가장 많이 사용되는 구조입니다. 코드에 대해 간단히 알아보면 Products테이블에서 ProductName이 ‘Chai’와 같은 상품을 출력하는 구문으로 그 결과는 IEnumerable<T>타입입니다. 그렇기 때문에 products변수는 IEnumerable<T>타입으로 유추 됩니다. 쿼리 표현식은 마지막 강좌에서 자세히 다루도록 할 것입니다.
2. 정말로 유추를 하는가?
간단한 예제 코드를 컴파일 하고 실제 어떻게 타입유추가 일어나는지를 확인 하기 위해 IL DisAssembler(ildasm.exe)를 사용하여 컴파일된 IL코드를 확인 해 보도록 하겠습니다.
아래는 Int타입과 직접 작성한 Person타입을 이용하는 예제 코드 입니다.
타입유추를 테스트 하기 위해 변수 i는 var키워드를 통해 초기화 했고 변수 b는 일반적인 방식으로 int타입으로 선언 하였습니다. 그리고 사용자 정의 타입인 Person타입을 변수 p에 할당 했습니다.
위의 코드를 컴파일 한 후 IL DisAssembler를 사용해 IL코드를 확인 해 보면 아래와 같은 코드를 볼 수 있습니다.

변수 i와 변수 b 모두 int32형태로 초기화 된 것을 확인 할 수 있으며 변수 p는 정확히 Person타입으로 유추된 것을 확인 할 수 있습니다.
3. var키워드의 사용 범위
var키워드는 아무데서나 사용할 수 있는 것은 아닙니다. 매서드 내부의 지역변수나 for문, foreach문, using문의 초기화 구문에서 사용될 수 있습니다.
매서드 내의 지역변수로서 사용
for문의 초기화 구문에서 사용
foreach문의 초기화 구문에서 사용
using문의 초기화 구문에서 사용
4. var키워드를 사용하면서 이것만은 주의하자.
var 키워드는 자바스크립트나 VB의 "Variant"로 오해할 수 있습니다. 하지만 C#의 var키워드는 런타임에 바인딩 되지 않고 컴파일 타임에 컴파일러가 적합한 타입을 결정하고 할당하게 됩니다.
그렇기 때문에 컴파일러가 적합한 타입을 결정하려면 선언과 동시에 초기화가 이루어 져야 하며 Null은 사용할 수 없습니다.(Null은 타입이 없기 때문이죠) 또한 클래스 범위에서는 사용할 수 없고 반드시 매서드 내의 지역변수로 사용해야 합니다.
var키워드의 상당히 편리하지만 명시적으로 타입이 선언되어 있지 않기 때문에 다른 개발자가 코드를 보게 되면 코드를 이해하기 난해 할 수 있습니다. var키워드를 반드시 필요한 경우(익명타입, 쿼리표현식의 결과타입, 중첩된 제네릭 타입 등)에 사용하면 보다 나은 개발 편의성 및 생산성 향상에 도움이 될 것입니다. 타입유추는 LINQ를 사용하기 위해 반드시 알아야 할 중요한 내용이기 때문에 첫번째 강좌에서 이렇게 다루었습니다. 다음 강좌는 익명타입 과 개체/컬렉션 초기화에 대해 알아 보도록 하겠습니다.
감사합니다.
| Excel 2007,2003 OLEDB 연결 문자열 (0) | 2012.12.16 |
|---|---|
| C#에서 OLEDB를 이용한 엑셀(EXCEL)파일 읽기 및 쓰기 (0) | 2012.12.16 |
| Loaded(로드완료) 이벤트 (0) | 2012.07.16 |
| 윈폼기반 프로그래밍을 할때 Invoke() 이쁘게쓰기! (0) | 2012.06.10 |
| Invoke , BeginInvoke, MethodInvoker (0) | 2012.06.10 |
You can use Mono's System.Xml for handling XML files but this requires including the System.Xml dll into your Unity program which increases its file size by about 1 MB. Not to mention the lack of documentation for using System.Xml on UnityScript.
I found rolling my own XML parser was easier. Note however that this is a really simple XML parser, it doesn't recognize attributes (I did not implement it simply because I don't use XML attributes).
using UnityEngine; using System.Collections; public class TinyXmlReader { private string xmlString = ""; private int idx = 0; public TinyXmlReader(string newXmlString) { xmlString = newXmlString; } public string tagName = ""; public bool isOpeningTag = false; public string content = ""; // properly looks for the next index of _c, without stopping at line endings, allowing tags to be break lines int IndexOf(char _c, int _i) { int i = _i; while (i < xmlString.Length) { if (xmlString[i] == _c) return i; ++i; } return -1; } public bool Read() { if (idx > -1) idx = xmlString.IndexOf("<", idx); if (idx == -1) { return false; } ++idx; // skip attributes, don't include them in the name! int endOfTag = IndexOf('>', idx); int endOfName = IndexOf(' ', idx); if ((endOfName == -1) || (endOfTag < endOfName)) { endOfName = endOfTag; } if (endOfTag == -1) { return false; } tagName = xmlString.Substring(idx, endOfName - idx); idx = endOfTag; // check if a closing tag if (tagName.StartsWith("/")) { isOpeningTag = false; tagName = tagName.Remove(0, 1); // remove the slash } else { isOpeningTag = true; } // if an opening tag, get the content if (isOpeningTag) { int startOfCloseTag = xmlString.IndexOf("<", idx); if (startOfCloseTag == -1) { return false; } content = xmlString.Substring(idx+1, startOfCloseTag-idx-1); content = content.Trim(); } return true; } // returns false when the endingTag is encountered public bool Read(string endingTag) { bool retVal = Read(); if (tagName == endingTag && !isOpeningTag) { retVal = false; } return retVal; } }
class TinyXmlReader { private var xmlString = ""; private var idx = 0; function TinyXmlReader(aXmlString : String) { xmlString = aXmlString; } var tagName = ""; var isOpeningTag = false; var content = ""; function Read() : boolean { idx = xmlString.IndexOf("<", idx); if (idx == -1) { return false; } ++idx; var endOfTag = xmlString.IndexOf(">", idx); if (endOfTag == -1) { return false; } tagName = xmlString.Substring(idx, endOfTag-idx); idx = endOfTag; // check if a closing tag if (tagName.StartsWith("/")) { isOpeningTag = false; tagName = tagName.Remove(0, 1); // remove the slash } else { isOpeningTag = true; } // if an opening tag, get the content if (isOpeningTag) { var startOfCloseTag = xmlString.IndexOf("<", idx); content = xmlString.Substring(idx+1, startOfCloseTag-idx-1); content = content.Trim(); } return true; } // returns false when the endingTag is encountered function Read(endingTag : String) : boolean { var retVal = Read(); if (tagName == endingTag && !isOpeningTag) { retVal = false; } return retVal; } }
Here I provide example code on how to use the TinyXmlReader.
private var text : String; var skin : GUISkin; function OnGUI() { GUILayout.Label(text, skin.label); } function Start() { var xmlText = System.IO.File.ReadAllText(Application.dataPath + "/Rifleman.xml"); var reader = TinyXmlReader(xmlText); while (reader.Read()) { if (reader.isOpeningTag) { text += (reader.tagName + " \"" + reader.content + "\"\n"); } if (reader.tagName == "Skills" && reader.isOpeningTag) { while(reader.Read("Skills")) // read as long as not encountering the closing tag for Skills { if (reader.isOpeningTag) { text += ("Skill: " + reader.tagName + " \"" + reader.content + "\"\n"); } } } } }
Plus, here's the XML file used for the example code: <xml> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <Unit> <Type>Rifleman</Type> <Label>ライフル銃兵 é (для Windows тоже!)</Label> <MaxHP>100</MaxHP> <SightRange>10</SightRange> <Skills> <UnitMovement> <Label>Move</Label> <Animation>move</Animation> <Range>10</Range> <Speed>6</Speed> </UnitMovement> <SimpleAttack> <Label>Attack</Label> <Animation>shoot</Animation> <Range>10</Range> <Damage>20</Damage> <AttackTime>0.348</AttackTime> <AttackType>Ranged</AttackType> </SimpleAttack> <Grenade> <Label>Throw Grenade</Label> <Animation>shoot</Animation> <Range>10</Range> <Damage>20</Damage> <AttackTime>0.348</AttackTime> <ExplosionRadius>5</ExplosionRadius> <NoOfUses>3</NoOfUses> </Grenade> </Skills> <Pahabol>oompa loompa doompity doo, we wouldn't hit that and neither should you</Pahabol> </Unit> </xml>
It produces this output:
엑셀 파일을 xml로 뽑아내는 방법인데 Attribute도 잘 뽑혀 나오는구나..
알아 놓을 겸 옮겨 놓음..
|
 Is your email address OK? You are signed up for our newsletters but your email address is either unconfirmed, or has not been reconfirmed in a long time. Please click here to have a confirmation email sent so we can confirm your email address and start sending you newsletters again. Alternatively, you can update your subscriptions.
Is your email address OK? You are signed up for our newsletters but your email address is either unconfirmed, or has not been reconfirmed in a long time. Please click here to have a confirmation email sent so we can confirm your email address and start sending you newsletters again. Alternatively, you can update your subscriptions.출처 : http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/14201/Converting-a-List-of-Data-to-XML-using-Microsoft-E
| 엑셀 데이터 시트를 xml로 출력 하기 -1(메모장 활용) (0) | 2012.12.09 |
|---|
메모장을 활용한 엑셀 데이터 시트를 xml로 출력 하기!!
일단 엑셀에 입력된 데이터 시트를 xml로 출력 하기 위해서는 맵핑이라는 작업을 해야합니다.
여기서 맵핑이란.. 제가 알기로는 데이터를 어떠한 방식으로 출력 할 것인지에 대한 규칙적인
형식이라고 해야하나 -_-;; 암튼 일단 출력할 엑셀 데이터 시트를 보겠습니다.
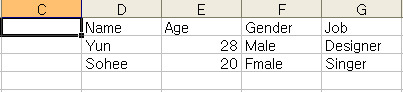
위 사진은 엑셀에 작성된 데이터들인데 맨 위가 필드 항목(속성이 되겠죠)들이고
그 아래에는 해당 속성의 값들이 되겠습니다.
자 이제 그럼 이 데이터들을 어떻게 맵핑 하느냐!!
일단 메모장을 열어서 아래와 같이 데이터를 입력 하시면 됩니다.
-----------------------------------------------------------
<test>
<Player>
<Name>1</Name>
<Age>1</Age>
<Gender>1</Gender>
<Jop>1</Jop>
</Player>
<Player>
<Name>2</Name>
<Age>2</Age>
<Gender>2</Gender>
<Jop>2</Jop>
</Player>
</test>
-----------------------------------------------------------
Html 처럼 각각의 태그 문장을 작성하면 되는데
<test> 이 부분은 xml의 노드 명칭을 작성하는 부분이 되겠습니다.
그리고 <Player> <Name>등 각 필드의 명을 작성하고 태그가 닫히는 사이에 아무 값을 넣어줍니다.
숫자를 넣으셔도 되고 문자를 넣으셔도 됩니다. (아무 데이터가 없을 경우 맵핑이 안됩니다.)
여기서 <test>태그 안에 다른 태그들을 중복으로 넣은 이유는 저 속성들이 여러개가 뽑힐 수 있기
때문에 중복적인 데이터 형식을 갖추기 위해 입력했습니다.
1개씩만 하면 나중에 맵핑이 제대로 안됩니다. 그러므로 꼭.. 최소 2개는 반복적으로 적어주세요.
작성을 완료 하신 후에 저장을 하는데 저장 하실 때 <다른 이름으로 저장>을 하셔서
아래 항목을 보시면 인코딩 방식이 있는데 꼭 UTF-8로 해 주십시오.
그래야 한글이든 영어든 안깨지고 잘 나옵니다 @_@;;
파일 형식은 TXT로 하되 파일 이름에 TEST.XML로 하시면 XML형태로 데이터가 저장 됩니다.
이렇게 메모장으로 내용을 작성하고 저장 한 후에 다시 엑셀로 돌아 갑니다.
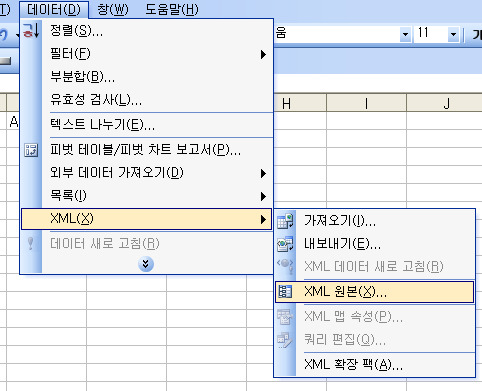
xml 형식으로 메모장에서 데이터를 저장 하고 난 뒤 엑셀의 메뉴에서
데이터>xml>xml원본 항목을 클릭 합니다.
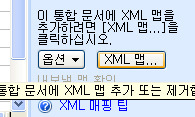
XML원본을 클릭하시게 되면 엑셀 우측 하단에 위와 같은 메뉴가 출력 되겠습니다.
메뉴 중 XML 맵.. 이라는 메뉴를 클릭 하시면 아래와 같은 그림이 출력 됩니다.
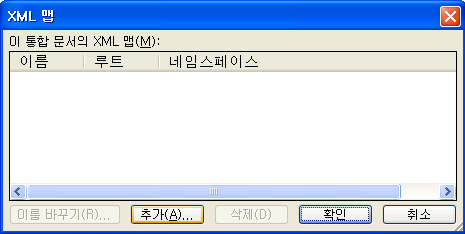
메뉴를 보시면 추가라는 항목이 있는데 이 추가 버튼을 눌러서 메모장에서 작성하여
저장한 test.xml 파일을 읽어 옵니다.
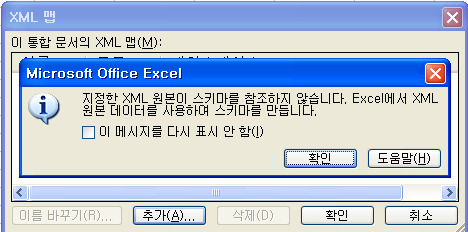
파일을 읽어오면 위와 같은 팝업창이 뜨는데 그냥 확인 하시면 됩니다.
메모장에서 작성 할 경우에는 스키마 형식이 저장이 안되기 때문에 그냥 확인 하셔도
자동으로 엑셀에서 생성을 해 줍니다. (다른 방법에서는 스키마 형식의 파일도 추출이 가능합니다.)
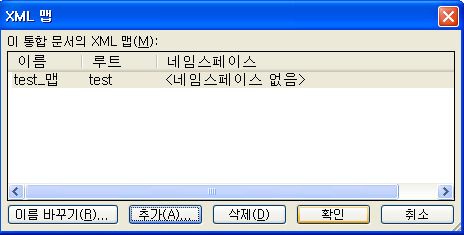
확인을 하고 나면 위 화면처럼 test_맵이라는 맵핑 요소가 생성 됐음을 알 수 있습니다.
그리고 확인을 누르게 되면 아래 그림과 같이 맵핑 요소가 생성 됐음을 알 수 있습니다.

맵핑 요소를 보시면 맨 위에 test 부분을 클릭하게 되면 하위 카테고리들이 한번에 지정이 됩니다.
그리고 test 글자 부분을 마우스로 드래그 하시면 맵핑 요소가 딸려 나오는걸 볼 수 있게 됩니다.
그리고 실제 자신이 출력 할 필드에 드랍을 하면 아래와 같이 맵핑이 완성이 되겠습니다.

맵핑을 한번 한 뒤에는 각 필드(속성)에 대한 값들은 추가가 가능합니다.
만약 필드(속성)을 추가 해야 할 경우에는 덮었던 맵핑 요소를 제거하고 맨위에 메모장 작성부터...
한번 하실때 잘 하셔야.. 합니다 그래야 노가다를 덜합니다 -_-;;
자 그럼 맵핑도 됐겠다 xml로 출력을 하도록 하겠습니다.

맵핑된 영역에 마우스를 갖다댄 뒤 마우스 우측 버튼을 눌러 메뉴를 출력 시킵니다.
그리고 xml>내보내기 버튼을 클릭 합니다.

내보내기를 누르게 되면 이제 저장할 xml의 파일명을 작성하면 됩니다.
파일명을 작성 한뒤 내보내기를 하게 되면 실제 사용 될 xml 파일이 완성이 됩니다.
아래는 출력한 xml의 내용입니다..
-----------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------
간단한? 방법으로 엑셀 데이터 시트를 xml로 출력 하는 방법에 대한 설명을 마치겠습니다.
[출처] 엑셀 데이터 시트를 xml로 출력 하기 -1(메모장 활용)|작성자 허수아비
| Converting a List of Data to XML using Microsoft Excel 2003 (0) | 2012.12.09 |
|---|
InvokeRepeating (함수명, 시작 시간, 함수호출 후 반복 간격);
MonoBehaviour.InvokeRepeating
Invokes the method methodName in time seconds.
After the first invocation repeats calling that function every repeatRate seconds.
// Starting in 2 seconds.
// a projectile will be launched every 0.3 seconds
var projectile : Rigidbody;
InvokeRepeating("LaunchProjectile", 2, 0.3);
function LaunchProjectile () {
var instance : Rigidbody = Instantiate(projectile);
instance.velocity = Random.insideUnitSphere * 5;
}
관련 함수 : http://docs.unity3d.com/Documentation/ScriptReference/MonoBehaviour.CancelInvoke.html
참조 : http://devkorea.co.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=m03_qna&wr_id=23031&sca=UNITY¤tId=44
출처 : http://docs.unity3d.com/Documentation/ScriptReference/MonoBehaviour.InvokeRepeating.html
| Using GUI slider to control animation on object (0) | 2013.01.27 |
|---|---|
| InGame Button (0) | 2012.12.14 |
| DisplayWizard(에디터로 쓸모가 많을 듯 한..) (0) | 2012.12.04 |
| Replace game object with prefab? (0) | 2012.12.04 |
| 폰트의 픽셀정보로 문자열을 Mesh들로 생성하여 보여주기 (0) | 2012.11.24 |
NGUI의 이벤트 함수를 SendMessage로 호출하려고 함수 원형을 찾아보고 올려놓음.
| 해상도에 맞게 UI 위치 조절 (0) | 2013.01.04 |
|---|---|
| 해상도에 맞게 UI Scale (0) | 2013.01.04 |
| NGUI Virtual Joystick (1) | 2012.12.05 |
| 스크롤/드래그 이벤트를 받는 방법 (0) | 2012.11.13 |
| 유니티 NGUI 에서 라벨에 한글(폰트) 적용하기 (2) | 2012.11.05 |
OnBecameVisible/OnBecameInvisible 이벤트 함수가 스크립트가 꺼져 있어도 상관없이 동작 한다길래,
신기해서 테스트 해보려고 Empty GameObject에 넣고 테스트 해봤는데 이벤트가 발생하질 않아서 뭔가 하고 찾아봤다.
OnBecameVisible/OnBecameInvisible 두 함수는 Renderer 관련 함수여서 Mesh Renderer Component가 추가 돼 있어야 이벤트가 발생한다.
삽질 좀 하고..
좀 유용하게 써먹어야겠다.
| C# 사용할때 주의할 점 (0) | 2013.01.15 |
|---|---|
| Expand/Collapse All(모두 펴기/접기) (0) | 2013.01.04 |
| iOS 프로젝트 포팅/최적화 팁 (0) | 2012.12.06 |
| 2D 게임을 위한 텍스쳐(Texture) 설정 (0) | 2012.11.28 |
| 성능 최적화 (0) | 2012.11.18 |
결과적으로 알파값이 0인 픽셀들도 원하는 테두리 색을 가지게 되어 보기 좋게 섞여진다.
More tips to follow soon.
| Expand/Collapse All(모두 펴기/접기) (0) | 2013.01.04 |
|---|---|
| OnBecameVisible/OnBecameInvisible (0) | 2012.12.06 |
| 2D 게임을 위한 텍스쳐(Texture) 설정 (0) | 2012.11.28 |
| 성능 최적화 (0) | 2012.11.18 |
| 유니티 게임개발하면서 알아낸 정보 정리. (0) | 2012.11.01 |
NGUI에서 제공하는(맞나? 홈페이지에서 찾아도 못찾겠는데..) 조이스틱이 있어서 구해서 올려놓음..
버전이 달라져서 그런지 좀 바꿔야 될 부분이 있다..
1. 우선 Import 하고나면 UIJoystick.cs가 별도의 Plugin 폴더에 빠져 있다.
이걸 NGUI-Scripts-UI 폴더로 옮겨주자.
2. UIJoystick.cs 스크립트에도 에러가 4개 난다.
파일을 열어서 아래 두가지를 수정해주자.
1) Tweener -> UITweener
2) UICamera.lastCamera -> UICamera.currentCamera
3. 예제의 조이스틱 컨트롤은 Layer가 Default가 아니라서 Culling Mask 때문에 조이스틱이 제대로 작동 안할 수 도 있다.
다른 Layer로 바꾸던지 Default로 바꾸자.(이것때문에 조작 안된다고 삽질을..)
위 까지만 수정하면 우선 돌아간다.
| 해상도에 맞게 UI Scale (0) | 2013.01.04 |
|---|---|
| NGUI: Events(Event Functions) (2) | 2012.12.07 |
| 스크롤/드래그 이벤트를 받는 방법 (0) | 2012.11.13 |
| 유니티 NGUI 에서 라벨에 한글(폰트) 적용하기 (2) | 2012.11.05 |
| NGUI - Sticky Floating Text (0) | 2012.10.28 |